Opportunity vs Necessity and Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
There are many reasons why a person becomes an entrepreneur, based on one of two common motivators in the form of opportunity-driven and necessity-driven entrepreneurship.1 Opportunity entrepreneurs are people who identify and pursue an opportunity (i.e., they choose to start a business over other careers), while necessity entrepreneurs are people who have no other options for work (i.e., they are compelled to start their own business because they have no other option). Understanding ones reason for becoming an entrepreneur is important to identify the necessary skills, knowledge, advice and support needed to improve their success rate.
In the case of opportunity-driven entrepreneurship, an individual pursues entrepreneurship based on identifying and exploiting opportunities. Individuals enter into entrepreneurship voluntarily because of interpersonal traits, intensions and aspirations. A major motivation behind opportunity-driven entrepreneurship is an individual’s passion to start a business rather than to be an employee.2 For such individuals, opportunity-driven entrepreneurship provides autonomy and encourages them to remain resilient in the pursuit of growing their business. This kind of entrepreneurship often results in businesses being growth orientated, profitable and focused on innovation and efficiency. In the case of necessity-driven entrepreneurship, an individual is forced into entrepreneurship as they have no other choice, most often due to high rates of unemployment and poverty. In this instance, an individual enters into entrepreneurship to become self-employed and to fulfil basic needs.
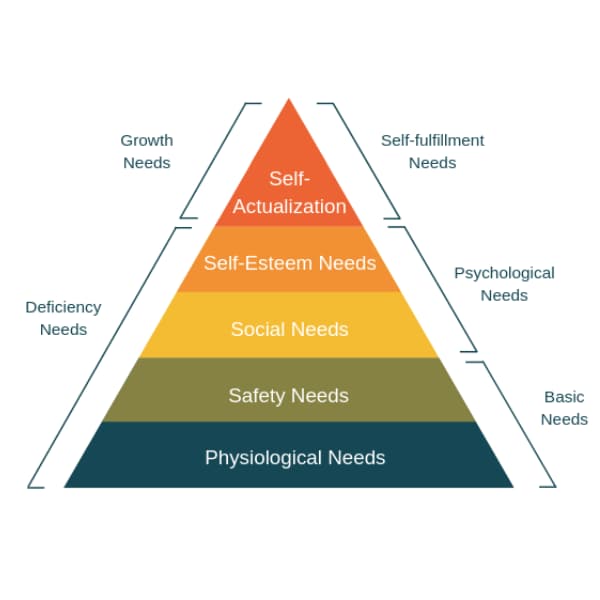
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory suggests that human needs can be categorized into five distinct categories including physiological needs, safety needs, love/belongingness needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization needs. Physiological needs are based on an individual’s basic needs such as food, shelter and clothing, safety needs are based on the need for job security, love and belongingness needs are based on the need to feel part of a family (community or team), esteem needs are based on the need for recognition, respect and status.3 Self-actualization occupies the topmost position in Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Model and is profound amongst entrepreneurs. Entrepreneurs are known to sacrifice all other needs in their pursuit of self-actualization, by turning their ideas into successful businesses.
1 Karadeniz and Ozdemir (2009), 2 Williams and Round (2009), 3 Cassar and Friedman (2009)
Image courtesy of: Nmilligan, CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0, via Wikimedia Commons






